Science
Conservation Efforts: Protecting USVI’s Natural Habitats
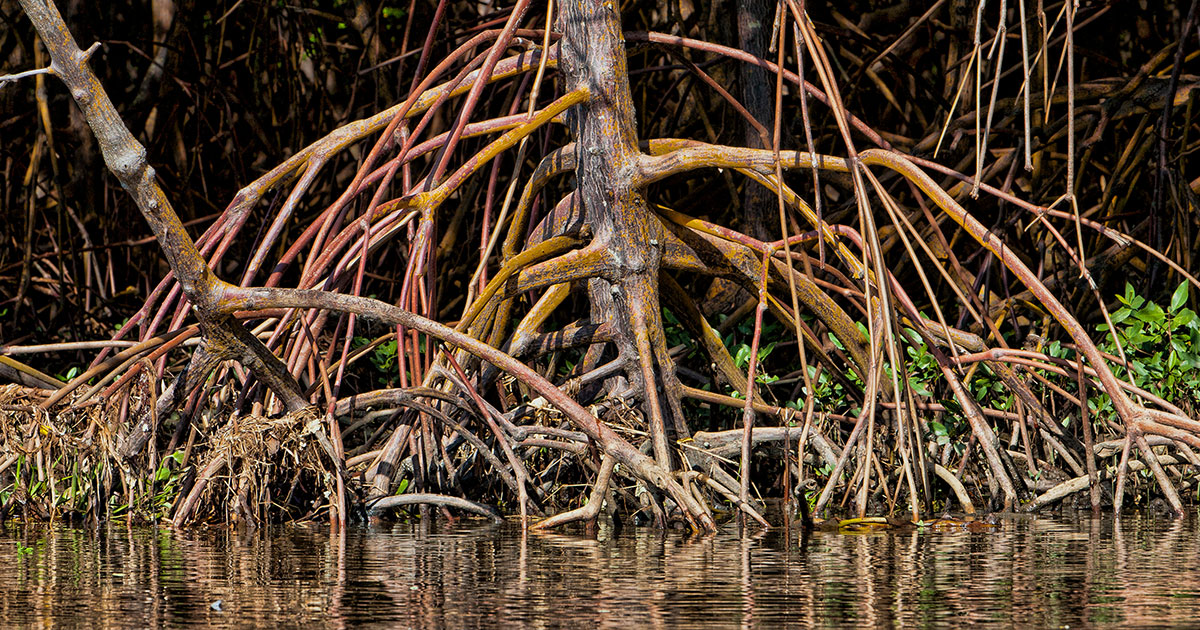

The U.S. Virgin Islands are renowned for their unique and diverse ecosystems, which include coral reefs, mangroves, and coastal forests. These habitats are not only crucial for the local biodiversity but also for the economy and well-being of the residents. However, they face significant threats from climate change, pollution, and human activities. Various conservation efforts are underway to protect and restore these natural habitats.
Coral Reef Conservation
The coral reefs of the USVI are among the most biologically diverse ecosystems in the world. These reefs provide habitat for numerous marine species and are vital for local fisheries and tourism. Unfortunately, they are highly vulnerable to climate change, particularly to rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification, which can lead to coral bleaching.
Efforts to protect these reefs involve comprehensive strategies to enhance their resilience. NOAA’s Coral Reef Conservation Program, in collaboration with the USVI Department of Planning and Natural Resources, has focused on identifying and prioritizing resilient coral reef areas. This includes mapping coral reef exposure to climate stressors and creating localized maps to highlight sensitive areas. Such data helps in implementing targeted conservation actions, such as protecting areas that are less susceptible to thermal stress and disease outbreaks (NCCOS Coastal Science Website) (NOAA Fisheries).
Mangrove Restoration
Mangroves are critical for coastal protection, water filtration, and providing nursery habitats for many marine species. In the USVI, these areas are threatened by coastal development and pollution. Restoration projects aim to rehabilitate degraded mangrove forests, often through community involvement and the use of native plant species.
One successful initiative is the re-establishment of mangrove buffers in areas prone to erosion and storm surges. These projects not only protect the coastline but also enhance biodiversity by providing habitats for various bird and marine species (Wildlife Conservation).
Sustainable Land Management
Land development poses a significant threat to natural habitats in the USVI. To mitigate this, sustainable land management practices are being promoted. This includes enforcing strict zoning regulations to limit construction in sensitive areas and encouraging sustainable agricultural practices to prevent land degradation.
For instance, efforts are made to integrate sustainable farming techniques, such as crop rotation and organic farming, which reduce the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers. These practices help maintain soil health and reduce runoff into the ocean, thereby protecting marine habitats (Wildlife Conservation).
Protected Areas and Marine Reserves
Establishing protected areas is a cornerstone of conservation efforts in the USVI. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are designated zones where human activities are regulated to preserve natural resources. Effective management of these areas has been shown to significantly increase biodiversity and biomass of marine species.
The USVI has several MPAs that serve to protect critical habitats and allow ecosystems to recover from human impact. These protected zones also serve as research sites to monitor the health of marine environments and the effectiveness of conservation strategies (National Geographic Society Newsroom).
Community Involvement and Education
Community involvement is crucial for the success of conservation efforts. Various programs focus on educating the local population about the importance of protecting natural habitats and engaging them in conservation activities. This includes beach clean-ups, tree planting, and citizen science projects where residents can participate in monitoring local wildlife and ecosystems.
Educational initiatives aim to foster a sense of stewardship among residents, ensuring that conservation efforts are sustained in the long term. By involving the community, these programs help build a collective effort towards protecting the natural heritage of the USVI (Wildlife Conservation).
Conclusion
Protecting the natural habitats of the USVI requires a multifaceted approach involving coral reef conservation, mangrove restoration, sustainable land management, establishment of protected areas, and community involvement. These efforts are essential for preserving the biodiversity and ecological integrity of the islands, which in turn supports the local economy and enhances the quality of life for its residents. Continued investment in and commitment to these conservation strategies will ensure that the natural beauty and resources of the USVI are preserved for future generations.
Science
USVI’s Contribution to Space Exploration Research

The U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI) is making noteworthy contributions to space exploration research, particularly through its unique astronomical resources and commitment to STEM education. The University of the Virgin Islands (UVI) plays a central role in these efforts, housing the Etelman Observatory on St. Thomas. This research facility, equipped with the Virgin Islands Robotic Telescope (VIRT), conducts vital astrophysical research, contributing to global efforts in space exploration and monitoring cosmic phenomena like gamma-ray bursts and gravitational waves.
In partnership with NASA, UVI also supports aerospace research through the Minority University Research and Education Program (MUREP). This initiative is focused on expanding research opportunities for minority-serving institutions, encouraging underrepresented students to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). UVI’s programs offer students hands-on experience in space-related fields, enhancing both local and national research efforts.
Furthermore, UVI’s innovation initiatives, like the 13D Research & Strategy Innovation Center, serve as a hub for creativity and technological advancement. The center fosters collaboration between students, researchers, and entrepreneurs, promoting projects in various disciplines, including space exploration technologies. This support structure aids in developing the next generation of leaders in space and technology.
Through these efforts, the USVI is not only contributing to space research but is also empowering a diverse group of students to engage with and innovate in the aerospace sector. The region’s strategic location, advanced research facilities, and educational programs position it as a growing player in global space exploration efforts.
Science
Technological Advances in USVI Agriculture

The agricultural sector in the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI) is experiencing a significant transformation through the adoption of modern technologies. These advancements are helping to increase productivity, promote sustainability, and support local farmers in overcoming the challenges of island farming. From smart farming tools to sustainable water management systems, technological innovations are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape in the Virgin Islands.
Smart Farming and Precision Agriculture
One of the most impactful technological advances in USVI agriculture is the rise of smart farming techniques and precision agriculture. Smart farming involves the use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, drones, and sensors to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. These tools enable farmers to make data-driven decisions that optimize yield, reduce waste, and conserve resources.
For example, sensors can be used to measure soil moisture levels, allowing farmers to adjust irrigation systems only when necessary. This not only saves water, but also ensures crops receive the precise amount of hydration they need for healthy growth. Drones equipped with imaging technology can monitor large fields, detecting issues such as pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies early on, helping farmers take quick and targeted action.
Hydroponics and Aquaponics: Sustainable Farming Solutions
Another key technological development gaining traction in the USVI is the use of hydroponic and aquaponic farming systems. These soil-free growing methods are ideal for islands like the Virgin Islands, where arable land and freshwater resources are limited. Hydroponics involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water, while aquaponics integrates fish farming with hydroponics, creating a symbiotic environment where fish waste provides nutrients for plants.
These systems not only conserve water but also allow for higher yields in smaller spaces. Additionally, they reduce the need for chemical fertilizers, promoting more sustainable and environmentally friendly farming practices. The rise of local hydroponic farms is providing fresh, locally grown produce to the Virgin Islands’ residents, reducing dependency on imported goods and strengthening food security.
Solar-Powered Technology for Sustainable Agriculture
Renewable energy is playing an increasingly important role in USVI agriculture, with solar-powered technologies helping farmers reduce costs and enhance sustainability. Solar panels are being installed on farms to power irrigation systems, greenhouses, and refrigeration units. This shift to renewable energy not only reduces electricity costs but also contributes to the island’s goal of reducing carbon emissions.
Solar-powered water pumps, for instance, are particularly beneficial in the Virgin Islands, where access to consistent and affordable electricity can be challenging for rural farmers. These systems can operate independently of the electrical grid, ensuring that farmers can irrigate their crops even in remote areas.
Vertical Farming: Maximizing Space and Yield
With limited arable land available, vertical farming is becoming an attractive option for agricultural innovation in the Virgin Islands. This method involves growing crops in stacked layers, typically indoors, using controlled-environment agriculture technology. By optimizing space and controlling environmental factors such as light, humidity, and temperature, vertical farming allows for year-round production, maximizing crop yield.
Vertical farming operations are particularly useful in urban settings, where land availability is restricted. They also help reduce transportation costs and carbon footprints, as produce can be grown close to consumers, reducing the reliance on imported goods.
Technology-Driven Support for Local Farmers
In addition to these technological innovations, local government and private organizations are working to provide farmers in the USVI with the tools and knowledge they need to adopt these advances. Training programs, grants, and workshops are helping farmers integrate new technologies into their operations, ensuring they can remain competitive in a changing agricultural landscape.
Organizations such as the University of the Virgin Islands’ Cooperative Extension Service (UVI CES) are playing a pivotal role in educating local farmers on best practices for incorporating technology into their farms. By providing hands-on training and access to modern tools, these programs are helping to future-proof the agricultural industry in the Virgin Islands.
Technological advances are revolutionizing the agricultural sector in the U.S. Virgin Islands, helping farmers increase productivity, reduce environmental impact, and overcome the challenges of island farming. From smart farming techniques to sustainable energy solutions, these innovations are empowering local farmers to produce more efficiently while promoting long-term sustainability. As these technologies continue to evolve, the future of agriculture in the Virgin Islands looks brighter than ever.
By embracing these advancements, the USVI is paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient agricultural industry, ensuring food security and economic growth for years to come.
Science
The Role of the U.S. Virgin Islands in Global Climate Research

The U.S. Virgin Islands, a tropical paradise in the Caribbean, is increasingly recognized for its critical role in global climate research. Nestled between the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, this small island territory provides scientists with an exceptional natural laboratory to study climate change impacts on marine ecosystems, coastal resilience, and biodiversity. As climate change accelerates worldwide, the unique geographical features and environmental challenges of the USVI make it a significant contributor to understanding climate dynamics, especially in tropical and marine environments.
A Hub for Marine and Environmental Research
One of the key areas where the USVI is making a mark is in marine research, particularly in studying coral reefs. The territory is home to some of the most vibrant coral reef ecosystems in the world, but these reefs are under significant threat from warming ocean temperatures, ocean acidification, and human activities. Scientists at the University of the Virgin Islands (UVI) and other research institutions are conducting groundbreaking studies on coral bleaching, reef restoration, and the broader impacts of climate change on marine biodiversity.
The UVI’s Center for Marine and Environmental Studies (CMES) plays a pivotal role in this effort. The center focuses on monitoring coral reef health, investigating the impacts of rising sea levels, and developing strategies to restore and protect these crucial ecosystems. Through partnerships with national and international organizations, researchers in the USVI contribute valuable data to global climate models, enhancing our understanding of how tropical ecosystems respond to environmental stressors.
Coastal Resilience and Sea Level Rise
As sea levels continue to rise due to the melting of polar ice and the thermal expansion of seawater, small island nations and territories like the USVI are on the front lines of coastal vulnerability. The islands’ low-lying areas and extensive coastline make them particularly susceptible to the impacts of rising seas, including coastal erosion, flooding, and habitat loss. This unique exposure allows the USVI to serve as a living laboratory for studying coastal resilience and adaptation strategies.
Researchers in the USVI are collaborating with international bodies to explore solutions for mitigating these challenges. By studying how coastal ecosystems like mangroves and seagrasses can help buffer against rising seas and storm surges, the territory contributes essential insights into natural solutions for climate adaptation. These studies are vital for developing sustainable strategies that can be applied to other vulnerable coastal regions around the world.
Renewable Energy Initiatives and Sustainability
In addition to its research contributions, the U.S. Virgin Islands is taking steps to reduce its own carbon footprint and enhance energy sustainability. Given the territory’s heavy reliance on imported fossil fuels, transitioning to renewable energy sources is not only an environmental imperative but also an economic necessity. The USVI government has committed to increasing the use of solar power, wind energy, and other renewable technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote energy independence.
Several solar energy projects, including those supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, are already underway in the territory. By transitioning to renewable energy, the USVI not only reduces its environmental impact but also sets an example for other island nations and regions striving for energy sustainability in the face of climate change. These renewable energy efforts are closely tied to global climate goals, as they aim to mitigate the effects of climate change by reducing reliance on carbon-intensive fuels.
Collaborative Global Research Networks
The USVI’s role in global climate research extends beyond its shores through participation in international networks and collaborations. The territory is part of various climate-focused initiatives, including the Caribbean Climate and Development Research Agenda, which aims to foster regional cooperation on climate resilience, adaptation, and mitigation. By sharing data, research findings, and expertise with other nations, the USVI plays a crucial part in the global response to climate change.
Additionally, the USVI collaborates with organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), and other global institutions. These partnerships allow the territory’s scientists and researchers to contribute to the global body of knowledge on climate change, while also benefiting from cutting-edge technologies and research techniques developed by their international peers.
The U.S. Virgin Islands has emerged as a key player in global climate research, leveraging its unique geography, ecosystems, and vulnerability to contribute valuable insights into climate change impacts and solutions. Through marine research, coastal resilience studies, renewable energy initiatives, and international collaborations, the USVI is helping to shape the global understanding of climate dynamics, particularly in tropical regions. As climate change continues to challenge communities worldwide, the contributions of the U.S. Virgin Islands will remain vital in the ongoing efforts to protect the planet’s future.
-

 Education1 year ago
Education1 year agoEducation Board Seeks Input on Schools Through Comprehensive Survey
-

 Education2 years ago
Education2 years agoCTE Board Enthusiastic About New Curriculum Standards, Yet Anxious Over Apprenticeship Support
-

 Crime2 years ago
Crime2 years agoRegistered Sex Offender Detained for Illegal Firearm Possession During Annual Surveillance Drive
-

 Videos3 years ago
Videos3 years ago2022 Gubernatorial Election: Voters Speak Out
-

 Development1 year ago
Development1 year agoCosts Surge as Donoe Estates Housing Project Resumes with New Contractor
-

 Videos3 years ago
Videos3 years agoGubernatorial Teams Celebrate St. Croix’s Bull & Bread Day
-

 Videos3 years ago
Videos3 years agoWakanda’s Female Might: A Dive into ‘Black Panther: Wakanda Forever’
-

 Crime2 years ago
Crime2 years agoSt. John’s Westin Resort Scene of Armed Robbery, Prompting Heightened Police Vigilance